KIT208 Assignment 4 Report_Group 4
Author:
Jigme Nidup Tenzin (559630)
Anh Quan Doan (624501)
Matthew Laughlin (620636)
Introduction:
Elevator pitch:
Have you ever spent hours moving the interior back and forth in order to figure out the best look for the house design while physically drained? This virtual reality designer training application will allow you to move the interior around your design effortlessly with different designing scenes to turn you into an interior design expert without breaking a sweat.
Description of the application
Description
The aim of this virtual reality (VR) interior design application is to give interior designers (students, juniors, experts, etc.) a tool for training in an immersive environment with a friendly user interface of the application accommodates a wide range of users from beginners to experienced. By conducting training in a 3D environment through a VR headset, the user will be able to manipulate objects, scale them, teleport within the space or to different designing scenes or levels, and import 3D objects from an interactive menu from this initial prototype..
Theoretical knowledge is based on the concept of how things are done and teaches you the experiences of others whereas practical knowledge gives hands-on learning experiences resulting in the best exposure of learning (Manish Ramnani, 2023).
This initial application provides:
- Easy access to learning materials. All learning materials can be easily accessed and free within the application by using an interactive importing menu without having to wait for the materials to arrive on site in real world training.
- Save time, space, and energy. The ease of moving furniture around, finding suitable pieces by simply importing from a menu, and teleporting to different locations in a designing scene or different levels improve usability and convenience compared to traditional methods.
- Immersive experience. The perception of 3D objects and house/room models from the application provokes the user's imagination and creativity by observing them relative to real-life scales with textures and colors that simulate real materials.
The final product will include current prototype features, additional sound effects, and lighting effects to further increase engagement, specifically different design levels with pressure to encourage critical thinking along with guidance on using the product. The light effect from sunlight as well as artificial house lights will bring different perceptions and visual feedback of the design to the user. Introducing sound effects of the surrounding area or interacting with 3D models within the application will provide audio feedback to enhance the immersive environment. Furthermore, having differently designed scenes, levels and other environments such as offices, commercial buildings, and stores will allow the user to have a variety of choices besides normal private houses, hence, providing a comprehensive training experience for the user.
Significance of this application
This application would be a great answer to current design training methods especially physically arranging interiors within a studio or through a 2D desktop interface. This application will overcome the limitations of reality where cost, time and materials must be considered and minimise resource demands while preserving the visual quality of traditional methods (Racz and Zilizi, 2018). Physical interior design training or the designing process in general requires resources such as instructors, interior pieces, an actual designing environment, and intensive imagination and physical capability to move objects around to the designer's liking. If learning was carried out without technology, then it would be more theoretical classes and little practical approaches. The computer with mouse and keyboard interface would solve much of the resource intensiveness of the traditional method, however, this does not bring the real visualization experience or perception due to unrealistic 2D/3D models, unreal scaled objects, inconvenience interactions of moving objects around using unhuman-like nature with little perception of lighting visual and audio. From studies conducted, visualization is highly essential for interior design and learning style has a significant impact on the skills of the students (Nussbaumer and Guerin, 2008).
This application solves these problems by providing:
- Unlimited hands-on experience. It would require an instructor on site to observe the apprentices which would limit the learning time where in this application, users can access the virtual application and work on their projects and get creative with their designs anytime.
- Immersive interactive training environment. It simulates real-life experiences with limitless designing options that can be compared with other designs with screenshots without the demand of physical resources.
- Unlimited mistakes. Typically, the procedure requires intense planning stage to reduce time and money expense and can only use image and imagination to visualise the final product. Users are not limited from any real-world requirements, therefore, boosting creativity.
- Improve learning curve. Rather than just listening and imagining to how things are done, users can experience it hand-on, significantly increasing interests and motiving them to boost their creativity.
- Lifting real world limiters. The ease of moving furniture around, finding suitable pieces by simply importing from a menu, and teleporting to change views or to different locations in a designing scene improves usability and convenience compared to traditional methods.
Leveraging digital building design, including cutting-edge tools like Virtual Reality (VR), is essential for preventing unnecessary construction and design miscommunication while revolutionizing the traditional design environment through interactive visual representation (Kaleja and Kozlovska, 2017).
Description of the interface solution :
Using VR as a solution for this application will merge the real perceptual experience from traditional interior design with the convenience and utilities of using desktop software to provide a comprehensive training program. VR allows users to immerse in a 3D environment from a first-person point of view, effectively provoking their visualization of the interior design compared to using the 2D monitor and desktop interface to inconvenience mouse and keyboard interactions. Furthermore, the dynamic realistic virtual environment allows the user to experience the representation of real-world objects/models relative to their scale, proportion, and spatial relationship, mimicking that real experience from traditional learning from designing studios. This helps deepen the user’s learning experience with their 3D interior design due to the high level of engagement with different interactions as well as the perception of space and less demand for visualization as the user can easily test different design layouts to their desire, therefore, enhancing the ability in making designing decision (Kaleja and Kozlovska, 2017).
The interaction with different objects using their virtual hands simulates the human nature of physically touching objects to boost the realistic experience, which is difficult to achieve using a 2D computer interface. The manipulation of objects and the ability to move with the 3D environment improve the trainees’ spatial awareness, again simulating human nature to make the experience more intuitive and interactive. The customization of object locations, size, and color through eye vision allows the user to achieve their design outcome.
The versatility of using VR allows the potential of introducing a different range of environments for designing from residential homes to restaurants, offices, and more. This brings a diversified and comprehensive training experience to support interior designers in their real-world projects.
The VR-only initial investment in the headset (where a classroom or institution can make a time purchase) is less capital intensive than the traditional set up of designing a room or studio as well as extensive revision and maintenance. Using VR would be a suitable choice of accessibility and affordability.
The process of constant revision and streamlining of physical interior design to achieve satisfied designs from the designers as well as trainers and clients is eliminated, making this process more effective. This is achieved because VR allows the user to experiment with different design layouts, combinations, sizes, styles, and more to ultimately have a better choice of design while limiting error in purchasing costs. By utilizing computer technology, simulation techniques, and sensing technology, this technology replicates real spaces, allowing users to intuitively partake in the design process and fully comprehend the spatial design's effects (Cao and Li, 2019).
Interaction Design:
Importing objects:
Allowing users to import objects from a menu is essential due to improve in accessibility and saves time. Having all these assets physically in one room or location would be impractical and time-consuming for the application. Importing objects from a menu improve productivity in the design process, enabling users to experiment with various elements efficiently.
Objects manipulation:
The ability to move objects within the virtual space is fundamental to interior design. One of the essence of interior design is arrangement furniture and decor to find the best layout. This feature allows users to experiment with different placements, helping them refine their designs and make informed decisions.
Objects scaling:
Users can scale the objects to the desired size. This gives the users the ability to determine the size of objects that will fit locations and the desired size to suit the scene. Users can customize the size of objects to match their vision and ensure that they fit within the scene, contributing to a more accurate and realistic design.
Teleporting and changing view:
Users can teleport to locations in the scene. This saves the user’s time of travel in the scene and makes it quicker to change from one location to another, especially when working on larger projects or in complex environments. It enables quick transitions between different areas of the design, enhancing productivity.
Proposed interactions:
- Changing colours of the furniture, tiles etc.
- Changing the lighting of the scene.
- Resizing and changing the layout of the house.
By implementing the above proposed interactions, it creates more learning space for the users to suit the scene to their design and not limit themselves. It provides more options in terms of designing tools which makes it more effective in the learning process.
Storyboard:
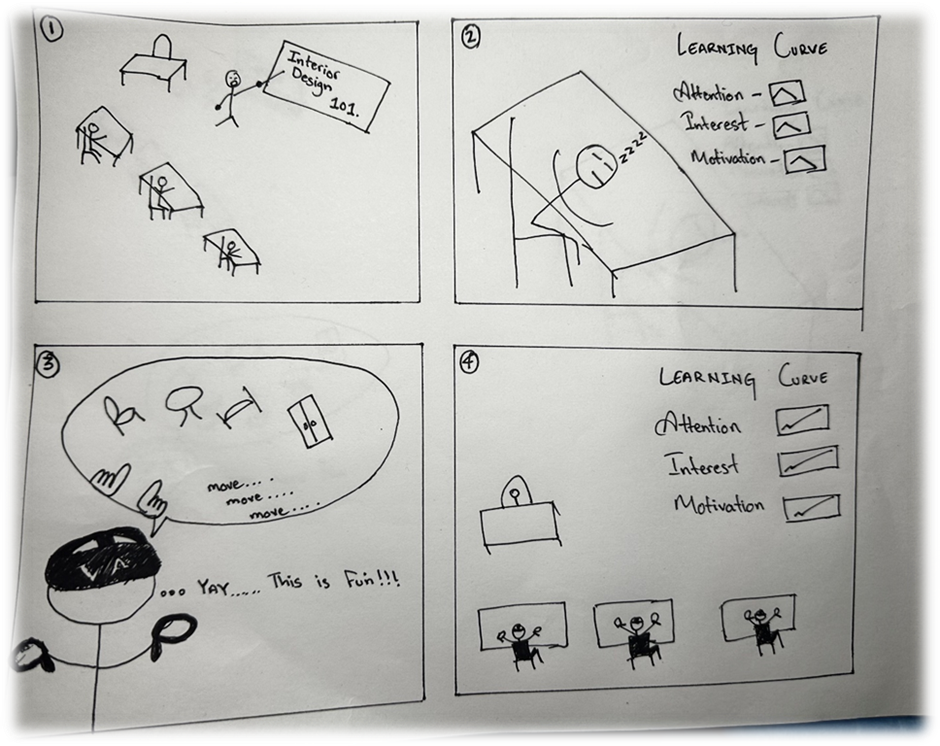
Technical Development:
Interface Technology: VR using Oculus Quest 1
- This is a VR headset kit by Oculus (a subsidiary of Meta Platforms) that allow the user to enter a VR environment wireless or connected. It also comes with 2 controllers to mimic human-hand interactions.
Development application: Unity
- A popular 2D and 3D gaming development application to great interactive content. It allows developments of interface technologies such as VR and AR.
Initial technical development:
Using VR for the application, it was required to build a scene. Scene is based on the intended theme (interior design). There are multiple objects (furniture) available on the scene and using the Oculus VR headset, it allows the user to dive in the VR software (unity) and interact with the objects, allowing them to change the interior design to their liking.
The development phase took four steps:
- First step, scene theme: The scene required a closed space with objects. A house module was used to save time building to test the application.
- Second step, objects: To suit the intended theme, furniture assets was used.
- Third step, moving and resizing: After importing the assets, the ability to move the objects around and resizing was implemented.
- Final step, teleporting: The application was ready for basic testing but to save the user’s time to travel from one room to another, changing scenes and teleporting were implemented.
- Bonus menu development: To further improve the user experience, a menu system with a list of furniture and scene was added so users can access the assets anytime.
Future development:
For the testing phase, the current application allows the user to choose, move and scale furniture and teleport to different locations. For the future updates, the application will include more designing tools like changing colours, room layout, lighting and adding sound effectives to give users a more realistic experience.
Initial 3D Models:


The 3D models used are:
- Tables, closets, sofas, chair, and bed.
- House
The theme being interior design, the obvious assets were the furniture and a house to complete the scene. Since it is a prototype, low- fidelity assets were used which was available free of cost.
For future development, the implementation of tiles in the application will significantly improve the designing approach where users can change or adapt to different tiles and match appropriate furniture.
Conclusion
It is aimed to allow the user to be creative and eliminate the limitations of traditional designing methods. With this application it will not only improve the learning experience but also the level of creativity where the number of designs will be infinite.
References:
Non-academic
Theoretical Knowledge Vs Practical Application https://vesim.ves.ac.in/vesimblog/student-blog/185-theoretical-knowledge-vs-practical-application.html
Academic
A. Racz and G. Zilizi, "VR Aided Architecture and Interior Design," 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing and Communication Engineering (ICACCE), Paris, France, 2018, pp. 11-16, doi: 10.1109/ICACCE.2018.8441714.
Cao, K. and Li, L., 2019, October. Research on the application of VR technology in interior design. In 2nd International Conference on Contemporary Education, Social Sciences and Ecological Studies (CESSES 2019) (pp. 745-748). Atlantis Press.
Nussbaumer, L.L. and Guerin, D.A. (2000), The Relationship Between Learning Styles and Visualization Skills Among Interior Design Students. Journal of Interior Design, 26: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-1668.2000.tb00355.x
Kaleja P. and Kozlovská M. (2017) Virtual Reality as Innovative Approach to the Interior Designing. Selected Scientific Papers - Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol.12 (Issue 1), pp. 109-116. https://doi.org/10.1515/sspjce-2017-0011
Asset
https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/environments/urban/modular-house-pack-1-236466
https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/props/furniture/furniture-free-pack-192628
https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/props/clothing/bed-pbr-227070
https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/tools/input-management/simple-vr-teleporter-115996
Polygon/Low Poly Materials - Lite | 2D Textures & Materials | Unity Asset Store
Appendices:
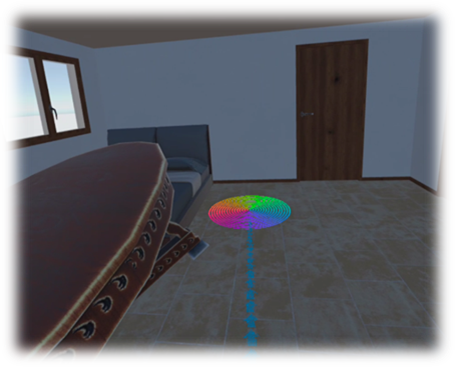
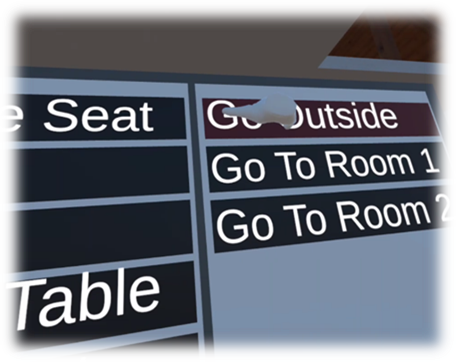
Application Screenshot
Choosing and moving furniture from menu.


Teleporting
Changing scene

Files
Get Interior Design Training VR Application
Interior Design Training VR Application
More posts
- KIT208 Assignment 5 Report_Group 4Oct 27, 2023